mirror of https://github.com/dynup/kpatch
459 lines
18 KiB
Markdown
459 lines
18 KiB
Markdown
kpatch: dynamic kernel patching
|
|
===============================
|
|
|
|
kpatch is a Linux dynamic kernel patching infrastructure which allows you to
|
|
patch a running kernel without rebooting or restarting any processes. It
|
|
enables sysadmins to apply critical security patches to the kernel immediately,
|
|
without having to wait for long-running tasks to complete, for users to log
|
|
off, or for scheduled reboot windows. It gives more control over uptime
|
|
without sacrificing security or stability.
|
|
|
|
kpatch is currently in active development. For now, it should _not_ be used
|
|
in production environments.
|
|
|
|
**WARNING: Use with caution! Kernel crashes, spontaneous reboots, and data loss
|
|
may occur!**
|
|
|
|
Here's a video of kpatch in action:
|
|
|
|
[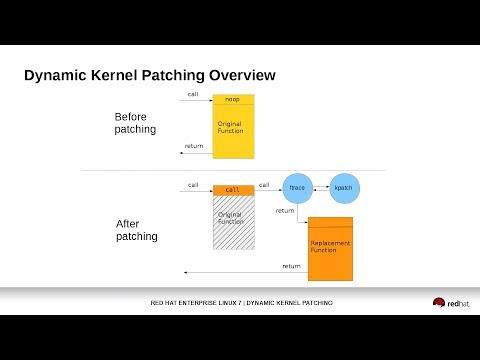](http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=juyQ5TsJRTA)
|
|
|
|
And a few more:
|
|
|
|
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rN0sFjrJQfU
|
|
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mftc80KyjA4
|
|
|
|
Installation
|
|
------------
|
|
|
|
###Prerequisites
|
|
|
|
####Fedora 20
|
|
|
|
*NOTE: You'll need about 15GB of free disk space for the kpatch-build cache in
|
|
`~/.kpatch` and for ccache.*
|
|
|
|
Install the dependencies for compiling kpatch:
|
|
|
|
sudo yum install gcc kernel-devel elfutils elfutils-devel
|
|
|
|
Install the dependencies for the "kpatch-build" command:
|
|
|
|
sudo yum install rpmdevtools pesign yum-utils
|
|
sudo yum-builddep kernel
|
|
sudo debuginfo-install kernel
|
|
|
|
# optional, but highly recommended
|
|
sudo yum install ccache
|
|
ccache --max-size=5G
|
|
|
|
####Ubuntu 14.04
|
|
|
|
*NOTE: You'll need about 15GB of free disk space for the kpatch-build cache in
|
|
`~/.kpatch` and for ccache.*
|
|
|
|
Install the dependencies for compiling kpatch:
|
|
|
|
apt-get install make gcc libelf-dev
|
|
|
|
Install the dependencies for the "kpatch-build" command:
|
|
|
|
apt-get install dpkg-dev
|
|
apt-get build-dep linux
|
|
|
|
# optional, but highly recommended
|
|
apt-get install ccache
|
|
ccache --max-size=5G
|
|
|
|
Install kernel debug symbols:
|
|
|
|
```bash
|
|
# Add ddebs repository
|
|
codename=$(lsb_release -sc)
|
|
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ddebs.list << EOF
|
|
deb http://ddebs.ubuntu.com/ ${codename} main restricted universe multiverse
|
|
deb http://ddebs.ubuntu.com/ ${codename}-security main restricted universe multiverse
|
|
deb http://ddebs.ubuntu.com/ ${codename}-updates main restricted universe multiverse
|
|
deb http://ddebs.ubuntu.com/ ${codename}-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
|
|
EOF
|
|
|
|
# add APT key
|
|
wget -Nq http://ddebs.ubuntu.com/dbgsym-release-key.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add -
|
|
apt-get update && apt-get install linux-image-$(uname -r)-dbgsym
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
####Debian 8.0
|
|
|
|
*NOTE: You'll need about 15GB of free disk space for the kpatch-build cache in
|
|
`~/.kpatch` and for ccache.*
|
|
|
|
Install the dependencies for compiling kpatch:
|
|
|
|
apt-get install make gcc libelf-dev build-essential
|
|
|
|
Install and prepare the kernel sources:
|
|
|
|
apt-get install linux-source-$(uname -r)
|
|
cd /usr/src && tar xvf linux-source-$(uname -r).tar.xz && ln -s linux-source-$(uname -r) linux && cd linux
|
|
cp /boot/config-$(uname -r) .config
|
|
for OPTION in CONFIG_KALLSYMS_ALL CONFIG_FUNCTION_TRACER ; do sed -i "s/# $OPTION is not set/$OPTION=y/g" .config ; done
|
|
sed -i "s/^SUBLEVEL.*/SUBLEVEL =/" Makefile
|
|
make -j`getconf _NPROCESSORS_CONF` deb-pkg KDEB_PKGVERSION=$(uname -r).9-1
|
|
|
|
Install the kernel packages and reboot
|
|
|
|
dpkg -i /usr/src/*.deb
|
|
reboot
|
|
|
|
Install the dependencies for the "kpatch-build" command:
|
|
|
|
apt-get install dpkg-dev
|
|
apt-get build-dep linux
|
|
|
|
# optional, but highly recommended
|
|
apt-get install ccache
|
|
ccache --max-size=5G
|
|
|
|
###Build
|
|
|
|
Compile kpatch:
|
|
|
|
make
|
|
|
|
###Install
|
|
|
|
OPTIONAL: Install kpatch to /usr/local:
|
|
|
|
sudo make install
|
|
|
|
Alternatively, the kpatch and kpatch-build scripts can be run directly from the
|
|
git tree.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Quick start
|
|
-----------
|
|
|
|
*NOTE: While kpatch is designed to work with any recent Linux
|
|
kernel on any distribution, the "kpatch-build" command currently only works on
|
|
Fedora 20 and Ubuntu 14.04.*
|
|
|
|
First, make a source code patch against the kernel tree using diff, git, or
|
|
quilt.
|
|
|
|
As a contrived example, let's patch /proc/meminfo to show VmallocChunk in ALL
|
|
CAPS so we can see it better:
|
|
|
|
$ cat meminfo-string.patch
|
|
Index: src/fs/proc/meminfo.c
|
|
===================================================================
|
|
--- src.orig/fs/proc/meminfo.c
|
|
+++ src/fs/proc/meminfo.c
|
|
@@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ static int meminfo_proc_show(struct seq_
|
|
"Committed_AS: %8lu kB\n"
|
|
"VmallocTotal: %8lu kB\n"
|
|
"VmallocUsed: %8lu kB\n"
|
|
- "VmallocChunk: %8lu kB\n"
|
|
+ "VMALLOCCHUNK: %8lu kB\n"
|
|
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_FAILURE
|
|
"HardwareCorrupted: %5lu kB\n"
|
|
#endif
|
|
|
|
Build the patch module:
|
|
|
|
$ kpatch-build -t vmlinux meminfo-string.patch
|
|
Using cache at /home/jpoimboe/.kpatch/3.13.10-200.fc20.x86_64/src
|
|
Testing patch file
|
|
checking file fs/proc/meminfo.c
|
|
Building original kernel
|
|
Building patched kernel
|
|
Detecting changed objects
|
|
Rebuilding changed objects
|
|
Extracting new and modified ELF sections
|
|
meminfo.o: changed function: meminfo_proc_show
|
|
Building patch module: kpatch-meminfo-string.ko
|
|
SUCCESS
|
|
|
|
> NOTE: The `-t vmlinux` option is used to tell `kpatch-build` to only look for
|
|
> changes in the `vmlinux` base kernel image, which is much faster than also
|
|
> compiling all the kernel modules. If your patch affects a kernel module, you
|
|
> can either omit this option to build everything, and have `kpatch-build`
|
|
> detect which modules changed, or you can specify the affected kernel build
|
|
> targets with multiple `-t` options.
|
|
|
|
That outputs a patch module named `kpatch-meminfo-string.ko` in the current
|
|
directory. Now apply it to the running kernel:
|
|
|
|
$ sudo kpatch load kpatch-meminfo-string.ko
|
|
loading core module: /usr/local/lib/modules/3.13.10-200.fc20.x86_64/kpatch/kpatch.ko
|
|
loading patch module: kpatch-meminfo-string.ko
|
|
|
|
Done! The kernel is now patched.
|
|
|
|
$ grep -i chunk /proc/meminfo
|
|
VMALLOCCHUNK: 34359337092 kB
|
|
|
|
How it works
|
|
------------
|
|
|
|
kpatch works at a function granularity: old functions are replaced with new
|
|
ones. It has four main components:
|
|
|
|
- **kpatch-build**: a collection of tools which convert a source diff patch to
|
|
a patch module. They work by compiling the kernel both with and without
|
|
the source patch, comparing the binaries, and generating a patch module
|
|
which includes new binary versions of the functions to be replaced.
|
|
|
|
- **patch module**: a kernel module (.ko file) which includes the
|
|
replacement functions and metadata about the original functions.
|
|
|
|
- **kpatch core module**: a kernel module (.ko file) which provides an
|
|
interface for the patch modules to register new functions for
|
|
replacement. It uses the kernel ftrace subsystem to hook into the original
|
|
function's mcount call instruction, so that a call to the original function
|
|
is redirected to the replacement function.
|
|
|
|
- **kpatch utility:** a command-line tool which allows a user to manage a
|
|
collection of patch modules. One or more patch modules may be
|
|
configured to load at boot time, so that a system can remain patched
|
|
even after a reboot into the same version of the kernel.
|
|
|
|
|
|
### kpatch-build
|
|
|
|
The "kpatch-build" command converts a source-level diff patch file to a kernel
|
|
patch module. Most of its work is performed by the kpatch-build script
|
|
which uses a utility named `create-diff-object` to compare changed objects.
|
|
|
|
The primary steps in kpatch-build are:
|
|
- Build the unstripped vmlinux for the kernel
|
|
- Patch the source tree
|
|
- Rebuild vmlinux and monitor which objects are being rebuilt.
|
|
These are the "changed objects".
|
|
- Recompile each changed object with `-ffunction-sections -fdata-sections`,
|
|
resulting in the changed patched objects
|
|
- Unpatch the source tree
|
|
- Recompile each changed object with `-ffunction-sections -fdata-sections`,
|
|
resulting in the changed original objects
|
|
- For every changed object, use `create-diff-object` to do the following:
|
|
* Analyze each original/patched object pair for patchability
|
|
* Add `.kpatch.funcs` and `.rela.kpatch.funcs` sections to the output object.
|
|
The kpatch core module uses this to determine the list of functions
|
|
that need to be redirected using ftrace.
|
|
* Add `.kpatch.dynrelas` and `.rela.kpatch.dynrelas` sections to the output object.
|
|
This will be used to resolve references to non-included local
|
|
and non-exported global symbols. These relocations will be resolved by the kpatch core module.
|
|
* Generate the resulting output object containing the new and modified sections
|
|
- Link all the output objects into a cumulative object
|
|
- Generate the patch module
|
|
|
|
### Patching
|
|
|
|
The patch modules register with the core module (`kpatch.ko`).
|
|
They provide information about original functions that need to be replaced, and
|
|
corresponding function pointers to the replacement functions.
|
|
|
|
The core module registers a handler function with ftrace. The
|
|
handler function is called by ftrace immediately before the original
|
|
function begins executing. This occurs with the help of the reserved mcount
|
|
call at the beginning of every function, created by the gcc `-mfentry` flag.
|
|
The ftrace handler then modifies the return instruction pointer (IP)
|
|
address on the stack and returns to ftrace, which then restores the original
|
|
function's arguments and stack, and "returns" to the new function.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Limitations
|
|
-----------
|
|
|
|
- Patches to functions which are always on the stack of at least one
|
|
process in the system are not supported. Examples: schedule(),
|
|
sys_poll(), sys_select(), sys_read(), sys_nanosleep(). Attempting to
|
|
apply such a patch will cause the insmod of the patch module to return
|
|
an error.
|
|
|
|
- Patches which modify init functions (annotated with `__init`) are not
|
|
supported. kpatch-build will return an error if the patch attempts
|
|
to do so.
|
|
|
|
- Patches which modify statically allocated data are not supported.
|
|
kpatch-build will detect that and return an error. (In the future
|
|
we will add a facility to support it. It will probably require the
|
|
user to write code which runs at patch module loading time which manually
|
|
updates the data.)
|
|
|
|
- Patches which change the way a function interacts with dynamically
|
|
allocated data might be safe, or might not. It isn't possible for
|
|
kpatch-build to verify the safety of this kind of patch. It's up to
|
|
the user to understand what the patch does, whether the new functions
|
|
interact with dynamically allocated data in a different way than the
|
|
old functions did, and whether it would be safe to atomically apply
|
|
such a patch to a running kernel.
|
|
|
|
- Patches which modify functions in vdso are not supported. These run in
|
|
user-space and ftrace can't hook them.
|
|
|
|
- Some incompatibilities currently exist between kpatch and usage of ftrace and
|
|
kprobes. See the Frequently Asked Questions section for more details.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Frequently Asked Questions
|
|
--------------------------
|
|
|
|
**Q. Isn't this just a virus/rootkit injection framework?**
|
|
|
|
kpatch uses kernel modules to replace code. It requires the `CAP_SYS_MODULE`
|
|
capability. If you already have that capability, then you already have the
|
|
ability to arbitrarily modify the kernel, with or without kpatch.
|
|
|
|
**Q. How can I detect if somebody has patched the kernel?**
|
|
|
|
When a patch module is loaded, the `TAINT_USER` flag is set. To test for it,
|
|
`cat /proc/sys/kernel/tainted` and check to see if the value of 64 has been
|
|
OR'ed in.
|
|
|
|
Eventually we hope to have a dedicated `TAINT_KPATCH` flag instead.
|
|
|
|
Note that the `TAINT_OOT_MODULE` flag (4096) will also be set, since the patch
|
|
module is built outside the Linux kernel source tree.
|
|
|
|
If your patch module is unsigned, the `TAINT_FORCED_MODULE` flag (2) will also
|
|
be set. Starting with Linux 3.15, this will be changed to the more specific
|
|
`TAINT_UNSIGNED_MODULE` (8192).
|
|
|
|
**Q. Will it destabilize my system?**
|
|
|
|
No, as long as the patch is chosen carefully. See the Limitations section
|
|
above.
|
|
|
|
**Q. Why does kpatch use ftrace to jump to the replacement function instead of
|
|
adding the jump directly?**
|
|
|
|
ftrace owns the first "call mcount" instruction of every kernel function. In
|
|
order to keep compatibility with ftrace, we go through ftrace rather than
|
|
updating the instruction directly. This approach also ensures that the code
|
|
modification path is reliable, since ftrace has been doing it successfully for
|
|
years.
|
|
|
|
**Q Is kpatch compatible with \<insert kernel debugging subsystem here\>?**
|
|
|
|
We aim to be good kernel citizens and maintain compatibility. A kpatch
|
|
replacement function is no different than a function loaded by any other kernel
|
|
module. Each replacement function has its own symbol name and kallsyms entry,
|
|
so it looks like a normal function to the kernel.
|
|
|
|
- **oops stack traces**: Yes. If the replacement function is involved in an
|
|
oops, the stack trace will show the function and kernel module name of the
|
|
replacement function, just like any other kernel module function. The oops
|
|
message will also show the taint flag (currently `TAINT_USER`).
|
|
- **kdump/crash**: Yes. Replacement functions are normal functions, so crash
|
|
will have no issues.
|
|
- **ftrace**: Yes, but certain uses of ftrace which involve opening the
|
|
`/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace` file or using `trace-cmd record` can result
|
|
in a tiny window of time where a patch gets temporarily disabled. Therefore
|
|
it's a good idea to avoid using ftrace on a patched system until this issue
|
|
is resolved.
|
|
- **systemtap/kprobes**: Some incompatibilities exist.
|
|
- If you setup a kprobe module at the beginning of a function before loading
|
|
a kpatch module, and they both affect the same function, kprobes "wins"
|
|
until the kprobe has been unregistered. This is tracked in issue
|
|
[#47](https://github.com/dynup/kpatch/issues/47).
|
|
- Setting a kretprobe before loading a kpatch module could be unsafe. See
|
|
issue [#67](https://github.com/dynup/kpatch/issues/67).
|
|
- **perf**: Yes.
|
|
- **tracepoints**: Patches to a function which uses tracepoints will result in
|
|
the tracepoints being effectively disabled as long as the patch is applied.
|
|
|
|
**Q. Why not use something like kexec instead?**
|
|
|
|
If you want to avoid a hardware reboot, but are ok with restarting processes,
|
|
kexec is a good alternative.
|
|
|
|
**Q. If an application can't handle a reboot, it's designed wrong.**
|
|
|
|
That's a good poi... [system reboots]
|
|
|
|
**Q. What changes are needed in other upstream projects?**
|
|
|
|
We hope to make the following changes to other projects:
|
|
|
|
- kernel:
|
|
- ftrace improvements to close any windows that would allow a patch to
|
|
be inadvertently disabled
|
|
- hot patch taint flag
|
|
- possibly the kpatch core module itself
|
|
|
|
- crash:
|
|
- point it to where the patch modules and corresponding debug symbols
|
|
live on the file system
|
|
|
|
**Q: Is it possible to register a function that gets called atomically with
|
|
`stop_machine` when the patch module loads and unloads?**
|
|
|
|
We do have plans to implement something like that.
|
|
|
|
**Q. What kernels are supported?**
|
|
|
|
kpatch needs gcc >= 4.8 and Linux >= 3.7 for use of the -mfentry flag.
|
|
|
|
**Q. Is it possible to remove a patch?**
|
|
|
|
Yes. Just run `kpatch unload` which will disable and unload the patch module
|
|
and restore the function to its original state.
|
|
|
|
**Q. Can you apply multiple patches?**
|
|
|
|
Yes, but to prevent any unexpected interactions between multiple patch modules,
|
|
it's recommended that you only have a single patch loaded at any given time.
|
|
This can be achieved by combining the new patch with the previous patch using
|
|
`combinediff` before running `kpatch-build`. You can then the `kpatch replace`
|
|
command to atomically replace the old patch module with the new cumulative one.
|
|
|
|
**Q. Why did kpatch-build detect a changed function that wasn't touched by the
|
|
source patch?**
|
|
|
|
There could be a variety of reasons for this, such as:
|
|
|
|
- The patch changed an inline function.
|
|
- The compiler decided to inline a changed function, resulting in the outer
|
|
function getting recompiled. This is common in the case where the inner
|
|
function is static and is only called once.
|
|
- The function uses a WARN() or WARN_ON() macro. These macros embed the source
|
|
code line number (`__LINE__`) into an instruction. If a function was changed
|
|
higher up in the file, it will affect the line numbers for all subsequent
|
|
WARN calls in the file, resulting in recompilation of their functions. If
|
|
this happens to you, you can usually just ignore it, as patching a few extra
|
|
functions isn't typically a problem. If it becomes a problem for whatever
|
|
reason, you can change the source patch to redefine the WARN macro for the
|
|
affected files, such that it hard codes the old line number instead of using
|
|
`__LINE__`, for example.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Get involved
|
|
------------
|
|
|
|
If you have questions or feedback, join the #kpatch IRC channel on freenode and
|
|
say hi. We also have a [mailing list](https://www.redhat.com/mailman/listinfo/kpatch).
|
|
|
|
Contributions are very welcome. Feel free to open issues or PRs on github.
|
|
For big PRs, it's a good idea to discuss them first in github issues or on the
|
|
[mailing list](https://www.redhat.com/mailman/listinfo/kpatch) before you write
|
|
a lot of code.
|
|
|
|
License
|
|
-------
|
|
|
|
kpatch is under the GPLv2 license.
|
|
|
|
This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
|
|
modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License
|
|
as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2
|
|
of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
|
|
|
|
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
|
|
but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
|
|
MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
|
|
GNU General Public License for more details.
|
|
|
|
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
|
|
along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
|
|
Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301, USA.
|